2024
Helmer, Philipp; Hottenrott, Sebastian; Wienböker, Kathrin; Pryss, Rüdiger; Drosos, Vasileios; Seitz, Anna Katharina; Röder, Daniel; Jovanovic, Aleksandar; Brugger, Jürgen; Kranke, Peter; Meybohm, Patrick; Winkler, Bernd E; Sammeth, Michael
Reliability of continuous vital sign monitoring in post-operative patients employing consumer-grade fitness trackers: A randomised pilot trial Journal Article
In: Digit Health, vol. 10, pp. 20552076241254026, 2024, ISSN: 2055-2076.
@article{pmid38746874,
title = {Reliability of continuous vital sign monitoring in post-operative patients employing consumer-grade fitness trackers: A randomised pilot trial},
author = {Philipp Helmer and Sebastian Hottenrott and Kathrin Wienböker and Rüdiger Pryss and Vasileios Drosos and Anna Katharina Seitz and Daniel Röder and Aleksandar Jovanovic and Jürgen Brugger and Peter Kranke and Patrick Meybohm and Bernd E Winkler and Michael Sammeth},
doi = {10.1177/20552076241254026},
issn = {2055-2076},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-01},
urldate = {2024-01-01},
journal = {Digit Health},
volume = {10},
pages = {20552076241254026},
abstract = {INTRODUCTION: Fitness trackers can provide continuous monitoring of vital signs and thus have the potential to become a complementary, mobile and effective tool for early detection of patient deterioration and post-operative complications.nnMETHODS: To evaluate potential implementations in acute care setting, we included 36 patients after moderate to major surgery in a recent randomised pilot trial to compare the performance of vital sign monitoring by three different fitness trackers (Apple Watch 7, Garmin Fenix 6pro and Withings ScanWatch) with established standard clinical monitors in post-anaesthesia care units and monitoring wards.nnRESULTS: During a cumulative period of 56 days, a total of 53,197 heart rate (HR) measurements, as well as 12,219 measurements of the peripheral blood oxygen saturation (SpO) and 28,954 respiratory rate (RR) measurements were collected by fitness trackers. Under real-world conditions, HR monitoring was accurate and reliable across all benchmarked devices (r = [0.95;0.98], < 0.001; Bias = [-0.74 bpm;-0.01 bpm]; MAPE∼2%). However, the performance of SpO (r = [0.21;0.68]; < 0.001; Bias = [-0.46%;-2.29%]; root-mean-square error = [2.82%;4.1%]) monitoring was substantially inferior. RR measurements could not be obtained for two of the devices, therefore exclusively the accuracy of the Garmin tracker could be evaluated (r = 0.28, < 0.001; Bias = -1.46/min). Moreover, the time resolution of the vital sign measurements highly depends on the tracking device, ranging from 0.7 to 117.94 data points per hour.nnCONCLUSION: According to the results of the present study, tracker devices are generally reliable and accurate for HR monitoring, whereas SpO and RR measurements should be interpreted carefully, considering the clinical context of the respective patients.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Sammeth, Michael; Mudra, Susann; Bialdiga, Sina; Hartmannsberger, Beate; Kramer, Sofia; Rittner, Heike
Comparative Methods for Demystifying Spatial Transcriptomics Book Chapter
In: Setubal, João Carlos; Stadler, Peter F.; Stoye, Jens (Ed.): Comparative Genomics, vol. 2802, pp. 515–546, Humana New York, NY, Methods Mol Biol, 2024, ISSN: 1940-6029.
@inbook{pmid38819570,
title = {Comparative Methods for Demystifying Spatial Transcriptomics},
author = {Michael Sammeth and Susann Mudra and Sina Bialdiga and Beate Hartmannsberger and Sofia Kramer and Heike Rittner},
editor = {João Carlos Setubal and Peter F. Stadler and Jens Stoye},
doi = {10.1007/978-1-0716-3838-5_17},
issn = {1940-6029},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-01-01},
urldate = {2024-01-01},
booktitle = {Comparative Genomics},
journal = {Methods Mol Biol},
volume = {2802},
pages = {515--546},
publisher = {Humana New York, NY},
edition = {Methods Mol Biol},
series = {Methods Mol Biol},
abstract = {Spatial Transcriptomics (ST), coined as the term for parallel RNA-Seq on cell populations ordered spatially on a histological tissue section, has recently become increasingly popular, especially in experiments where microfluidics-based single-cell sequencing fails, such as assays on neurons. ST platforms, like the 10x Visium technology investigated herein, therefore produce in a single experiment simultaneously thousands of RNA readouts, captured by an array of micrometer scale spots under the histological section. Therefore, a central challenge of analyzing ST experiments consists of analyzing the gene expression morphology of all spots to delineate clusters of similar cell mixtures, which are then compared to each other to identify up- or down-regulated marker genes. Moreover, another level of complexity in ST experiments, compared to traditional RNA-Seq, is imposed by staining the tissue section with protein markers of cells or cell components to identify spots providing relevant information afterward. The corresponding microscopy images need to be analyzed in addition to the RNA-Seq read mappings on the reference genome and transcriptome sequences. Focusing on the software suite provided by the Visium platform manufacturer, we break down the ST analysis pipeline into its four essential steps-the image analysis, the read alignment, the gene quantification, and the spot clustering-and compare results obtained when using reads from different subsets of spots and/or when employing alternative genome or transcriptome references. Our comparative analyses demonstrate the impact of spot selection and the choice of genome/transcriptome references on the analysis results when employing the manufacturer's pipeline.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2023
Helmer, Philipp; Rodemers, Philipp; Hottenrott, Sebastian; Leppich, Robert; Helwich, Maja; Pryss, Rüdiger; Kranke, Peter; Meybohm, Patrick; Winkler, Bernd E; Sammeth, Michael
Evaluating blood oxygen saturation measurements by popular fitness trackers in postoperative patients: A prospective clinical trial Journal Article
In: iScience, vol. 26, no. 11, pp. 108155, 2023, ISSN: 2589-0042.
@article{pmid37876822,
title = {Evaluating blood oxygen saturation measurements by popular fitness trackers in postoperative patients: A prospective clinical trial},
author = {Philipp Helmer and Philipp Rodemers and Sebastian Hottenrott and Robert Leppich and Maja Helwich and Rüdiger Pryss and Peter Kranke and Patrick Meybohm and Bernd E Winkler and Michael Sammeth},
doi = {10.1016/j.isci.2023.108155},
issn = {2589-0042},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-11-01},
urldate = {2023-11-01},
journal = {iScience},
volume = {26},
number = {11},
pages = {108155},
abstract = {Blood oxygen saturation is an important clinical parameter, especially in postoperative hospitalized patients, monitored in clinical practice by arterial blood gas (ABG) and/or pulse oximetry that both are not suitable for a long-term continuous monitoring of patients during the entire hospital stay, or beyond. Technological advances developed recently for consumer-grade fitness trackers could-at least in theory-help to fill in this gap, but benchmarks on the applicability and accuracy of these technologies in hospitalized patients are currently lacking. We therefore conducted at the postanaesthesia care unit under controlled settings a prospective clinical trial with 201 patients, comparing in total >1,000 oxygen blood saturation measurements by fitness trackers of three brands with the ABG gold standard and with pulse oximetry. Our results suggest that, despite of an overall still tolerable measuring accuracy, comparatively high dropout rates severely limit the possibilities of employing fitness trackers, particularly during the immediate postoperative period of hospitalized patients.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Sammeth, Michael; Ursache, Nicu-Cosmin; Alboaie, Sînică
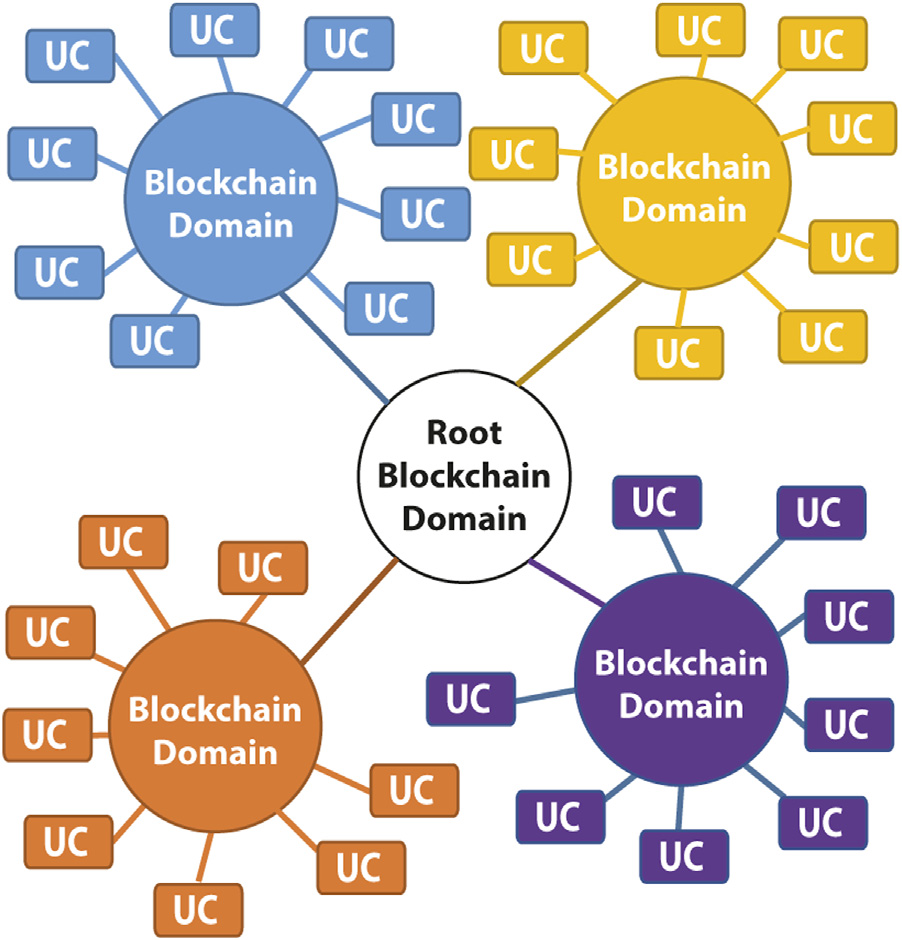
OpenDSU: digital sovereignty in PharmaLedger Journal Article
In: Front. Blockchain, vol. 6, 2023, ISSN: 2624-7852.
@article{Sammeth2023,
title = {OpenDSU: digital sovereignty in PharmaLedger},
author = {Michael Sammeth and Nicu-Cosmin Ursache and Sînică Alboaie},
doi = {10.3389/fbloc.2023.1126978},
issn = {2624-7852},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-06-15},
urldate = {2023-06-15},
journal = {Front. Blockchain},
volume = {6},
publisher = {Frontiers Media SA},
abstract = {<jats:p><jats:bold>Introduction:</jats:bold> Distributed ledger networks, chiefly those based on blockchain technologies, currently are heralding a next-generation of computer systems that aims to suit modern users’ demands. Over the recent years, several technologies for blockchains, off-chaining strategies, as well as decentralised and respectively self-sovereign identity systems have shot up so fast that standardisation of the protocols is lagging behind, severely hampering the interoperability of different approaches. Moreover, most of the currently available solutions for distributed ledgers focus on either home users or enterprise use case scenarios, failing to provide integrative solutions addressing the needs of both.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Methods:</jats:bold> Herein, we introduce the OpenDSU platform that allows to interoperate generic blockchain technologies, organised–and possibly cascaded in a hierarchical fashion–in domains. To achieve this flexibility, we seamlessly integrated a set of well conceived components that orchestrate off-chain data and provide granularly resolved and cryptographically secure access levels, intrinsically nested with sovereign identities across the different domains. The source code and extensive documentation of all OpenDSU components described herein are publicly available under the MIT open-source licence at <jats:ext-link>https://opendsu.com</jats:ext-link>.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold> Employing our platform to PharmaLedger, an inter-European network for the standardisation of data handling in the pharmaceutical industry and in healthcare, we demonstrate that OpenDSU can cope with generic demands of heterogeneous use cases in both, performance and handling substantially different business policies.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Discussion:</jats:bold> Importantly, whereas available solutions commonly require a pre-defined and fixed set of components, no such vendor lock-in restrictions on the blockchain technology or identity system exist in OpenDSU, making systems built on it flexibly adaptable to new standards evolving in the future.</jats:p>},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2022
Helmer, Philipp; Hottenrott, Sebastian; Rodemers, Philipp; Leppich, Robert; Helwich, Maja; Pryss, Rüdiger; Kranke, Peter; Meybohm, Patrick; Winkler, Bernd E; Sammeth, Michael
In: J Med Internet Res, vol. 24, no. 12, pp. e42359, 2022, ISSN: 1438-8871.
@article{pmid36583938,
title = {Accuracy and Systematic Biases of Heart Rate Measurements by Consumer-Grade Fitness Trackers in Postoperative Patients: Prospective Clinical Trial},
author = {Philipp Helmer and Sebastian Hottenrott and Philipp Rodemers and Robert Leppich and Maja Helwich and Rüdiger Pryss and Peter Kranke and Patrick Meybohm and Bernd E Winkler and Michael Sammeth},
doi = {10.2196/42359},
issn = {1438-8871},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-12-01},
urldate = {2022-12-01},
journal = {J Med Internet Res},
volume = {24},
number = {12},
pages = {e42359},
abstract = {BACKGROUND: Over the recent years, technological advances of wrist-worn fitness trackers heralded a new era in the continuous monitoring of vital signs. So far, these devices have primarily been used for sports.nnOBJECTIVE: However, for using these technologies in health care, further validations of the measurement accuracy in hospitalized patients are essential but lacking to date.nnMETHODS: We conducted a prospective validation study with 201 patients after moderate to major surgery in a controlled setting to benchmark the accuracy of heart rate measurements in 4 consumer-grade fitness trackers (Apple Watch 7, Garmin Fenix 6 Pro, Withings ScanWatch, and Fitbit Sense) against the clinical gold standard (electrocardiography).nnRESULTS: All devices exhibited high correlation (r≥0.95; P<.001) and concordance (r≥0.94) coefficients, with a relative error as low as mean absolute percentage error <5% based on 1630 valid measurements. We identified confounders significantly biasing the measurement accuracy, although not at clinically relevant levels (mean absolute error<5 beats per minute).nnCONCLUSIONS: Consumer-grade fitness trackers appear promising in hospitalized patients for monitoring heart rate.nnTRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05418881; https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05418881.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Helmer, Philipp; Helf, Daniel; Sammeth, Michael; Winkler, Bernd; Hottenrott, Sebastian; Meybohm, Patrick; Kranke, Peter
In: J Clin Med, vol. 11, no. 15, 2022, ISSN: 2077-0383.
@article{pmid35956113,
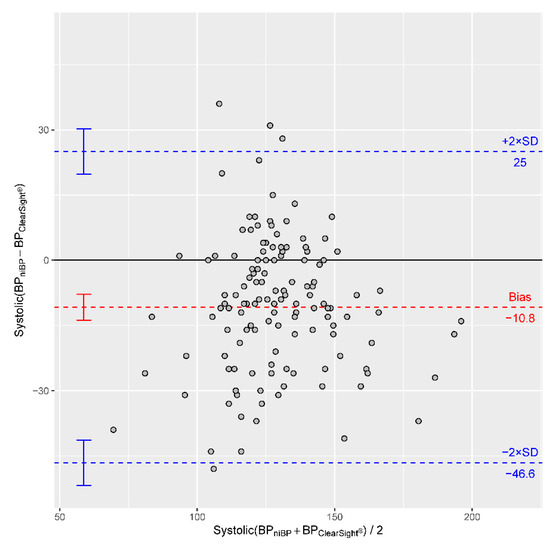
title = {The Use of Non-Invasive Continuous Blood Pressure Measuring (ClearSight) during Central Neuraxial Anaesthesia for Caesarean Section-A Retrospective Validation Study},
author = {Philipp Helmer and Daniel Helf and Michael Sammeth and Bernd Winkler and Sebastian Hottenrott and Patrick Meybohm and Peter Kranke},
doi = {10.3390/jcm11154498},
issn = {2077-0383},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-08-01},
urldate = {2022-08-01},
journal = {J Clin Med},
volume = {11},
number = {15},
abstract = {The close monitoring of blood pressure during a caesarean section performed under central neuraxial anaesthesia should be the standard of safe anaesthesia. As classical oscillometric and invasive blood pressure measuring have intrinsic disadvantages, we investigated a novel, non-invasive technique for continuous blood pressure measuring. In this monocentric, retrospective data analysis, the reliability of continuous non-invasive blood pressure measuring using ClearSight (Edwards Lifesciences Corporation) is validated in 31 women undergoing central neuraxial anaesthesia for caesarean section. In addition, patients and professionals evaluated ClearSight through questioning. 139 measurements from 11 patients were included in the final analysis. Employing Bland-Altman analyses, we identified a bias of -10.8 mmHg for systolic, of -0.45 mmHg for diastolic and of +0.68 mmHg for mean arterial blood pressure measurements. Pooling all paired measurements resulted in a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.7 for systolic, of 0.67 for diastolic and of 0.75 for mean arterial blood pressure. Compensating the interindividual differences in linear regressions of the paired measurements provided improved correlation coefficients of 0.73 for systolic, of 0.9 for diastolic and of 0.89 for mean arterial blood pressure measurements. Diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure are within an acceptable range of deviation from the reference method, according to the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) in the patient collective under study. Both patients and professionals prefer ClearSight to oscillometric blood pressure measurement in regard of comfort and handling.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2021
Coelho, Vitor Lima; de Brito, Tarcísio Fontenele; de Abreu Brito, Ingrid Alexandre; Cardoso, Maira Arruda; Berni, Mateus Antonio; Araujo, Helena Maria Marcolla; Sammeth, Michael; Pane, Attilio
Analysis of ovarian transcriptomes reveals thousands of novel genes in the insect vector Rhodnius prolixus Journal Article
In: Sci Rep, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 1918, 2021, ISSN: 2045-2322.
@article{pmid33479356,
title = {Analysis of ovarian transcriptomes reveals thousands of novel genes in the insect vector Rhodnius prolixus},
author = {Vitor Lima Coelho and Tarcísio Fontenele de Brito and Ingrid Alexandre de Abreu Brito and Maira Arruda Cardoso and Mateus Antonio Berni and Helena Maria Marcolla Araujo and Michael Sammeth and Attilio Pane},
doi = {10.1038/s41598-021-81387-1},
issn = {2045-2322},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-01},
urldate = {2021-01-01},
journal = {Sci Rep},
volume = {11},
number = {1},
pages = {1918},
abstract = {Rhodnius prolixus is a Triatominae insect species and a primary vector of Chagas disease. The genome of R. prolixus has been recently sequenced and partially assembled, but few transcriptome analyses have been performed to date. In this study, we describe the stage-specific transcriptomes obtained from previtellogenic stages of oogenesis and from mature eggs. By analyzing ~ 228 million paired-end RNA-Seq reads, we significantly improved the current genome annotations for 9206 genes. We provide extended 5' and 3' UTRs, complete Open Reading Frames, and alternative transcript variants. Strikingly, using a combination of genome-guided and de novo transcriptome assembly we found more than two thousand novel genes, thus increasing the number of genes in R. prolixus from 15,738 to 17,864. We used the improved transcriptome to investigate stage-specific gene expression profiles during R. prolixus oogenesis. Our data reveal that 11,127 genes are expressed in the early previtellogenic stage of oogenesis and their transcripts are deposited in the developing egg including key factors regulating germline development, genome integrity, and the maternal-zygotic transition. In addition, GO term analyses show that transcripts encoding components of the steroid hormone receptor pathway, cytoskeleton, and intracellular signaling are abundant in the mature eggs, where they likely control early embryonic development upon fertilization. Our results significantly improve the R. prolixus genome and transcriptome and provide novel insight into oogenesis and early embryogenesis in this medically relevant insect.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2019
Brant, Ayslan C; Menezes, Albert N; Felix, Shayany P; de Almeida, Liz M; Sammeth, Michael; Moreira, Miguel A M
In: Genomics, vol. 111, no. 6, pp. 1853–1861, 2019, ISSN: 1089-8646.
@article{pmid30552977,
title = {Characterization of HPV integration, viral gene expression and E6E7 alternative transcripts by RNA-Seq: A descriptive study in invasive cervical cancer},
author = {Ayslan C Brant and Albert N Menezes and Shayany P Felix and Liz M de Almeida and Michael Sammeth and Miguel A M Moreira},
doi = {10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.12.008},
issn = {1089-8646},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-12-01},
journal = {Genomics},
volume = {111},
number = {6},
pages = {1853--1861},
abstract = {Scarce data are available on the expression of papillomavirus genome and the frequency of alternatively spliced E6E7 mRNAs in invasive cervical cancer. We carried out a comprehensive characterization of HPV expression by RNA-Seq analysis in 22 invasive cervical cancer with HPV16 or HPV18, characterizing the presence of integrated/episomal viral DNA, the integration sites in human genome and the proportion of alternative splicing products of E6 and E7 genes. The expression patterns suggested the presence of episomal and/or integrated viral DNA, with integration detected in most tumors, frequently occurring within human genes in HPV18+ and in intergenic regions in HPV16+ tumors. Alternative splicing of E6E7 transcripts showed E6*I as the most frequent isoform for both viral types, followed by E6*II and E6/E7 (unspliced) transcripts in HPV16+, and by E6/E7 in HPV18+ tumors. Previously described E6*VI and E6*V transcript isoforms for HPV16, and E6*X for HPV18, were rare or not detected.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Carvalho, Eduardo B; Ramos, Isalira P R; Nascimento, Alvaro F S; Brasil, Guilherme V; Mello, Debora B; Oti, Martin; Sammeth, Michael; Bahia, Maria T; de Carvalho, Antonio C Campos; Carvalho, Adriana B
Echocardiographic Measurements in a Preclinical Model of Chronic Chagasic Cardiomyopathy in Dogs: Validation and Reproducibility Journal Article
In: Front Cell Infect Microbiol, vol. 9, pp. 332, 2019, ISSN: 2235-2988.
@article{pmid31616643,
title = {Echocardiographic Measurements in a Preclinical Model of Chronic Chagasic Cardiomyopathy in Dogs: Validation and Reproducibility},
author = {Eduardo B Carvalho and Isalira P R Ramos and Alvaro F S Nascimento and Guilherme V Brasil and Debora B Mello and Martin Oti and Michael Sammeth and Maria T Bahia and Antonio C Campos de Carvalho and Adriana B Carvalho},
doi = {10.3389/fcimb.2019.00332},
issn = {2235-2988},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-01-01},
journal = {Front Cell Infect Microbiol},
volume = {9},
pages = {332},
abstract = { The failure to translate preclinical results to the clinical setting is the rule, not the exception. One reason that is frequently overlooked is whether the animal model reproduces distinctive features of human disease. Another is the reproducibility of the method used to measure treatment effects in preclinical studies. Left ventricular (LV) function improvement is the most common endpoint in preclinical cardiovascular disease studies, while echocardiography is the most frequently used method to evaluate LV function. In this work, we conducted a robust echocardiographic evaluation of LV size and function in dogs chronically infected by . Echocardiography was performed blindly by two distinct observers in mongrel dogs before and between 6 and 9 months post infection. Parameters analyzed included end-systolic volume (ESV), end-diastolic volume (EDV), ejection fraction (EF), and fractional shortening (FS). We observed a significant LVEF and FS reduction in infected animals compared to controls, with no significant variation in volumes. However, the effect of chronic infection in systolic function was quite variable, with EF ranging from 17 to 66%. Using the cut-off value of EF ≤ 40%, established for dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) in dogs, only 28% of the infected dogs were affected by the chronic infection. The canine model of CCC mimics human disease, reproducing the percentage of individuals that develop heart failure during the chronic infection. It is thus mandatory to establish inclusion criteria in the experimental design of canine preclinical studies to account for the variable effect that chronic infection has on systolic function.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2018
Coelho, Vitor; Sammeth, Michael
An automated method for detecting alternatively spliced protein domains Journal Article
In: Bioinformatics, vol. 34, no. 22, pp. 3809–3816, 2018, ISSN: 1367-4811.
@article{pmid29868795,
title = {An automated method for detecting alternatively spliced protein domains},
author = {Vitor Coelho and Michael Sammeth},
doi = {10.1093/bioinformatics/bty425},
issn = {1367-4811},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-11-01},
journal = {Bioinformatics},
volume = {34},
number = {22},
pages = {3809--3816},
abstract = {MOTIVATION: Alternative splicing (AS) has been demonstrated to play a role in shaping eukaryotic gene diversity at the transcriptional level. However, the impact of AS on the proteome is still controversial. Studies that seek to explore the effect of AS at the proteomic level are hampered by technical difficulties in the cumbersome process of casting forth and back between genome, transcriptome and proteome space coordinates, and the naïve prediction of protein domains in the presence of AS suffers many redundant sequence scans that emerge from constitutively spliced regions that are shared between alternative products of a gene.nnRESULTS: We developed the AstaFunk pipeline that computes for every generic transcriptome all domains that are altered by AS events in a systematic and efficient manner. In a nutshell, our method employs Viterbi dynamic programming, which guarantees to find all score-optimal hits of the domains under consideration, while complementary optimizations at different levels avoid redundant and other irrelevant computations. We evaluate AstaFunk qualitatively and quantitatively using RNAseq in well-studied genes with AS, and on large-scale employing entire transcriptomes. Our study confirms complementary reports that the effect of most AS events on the proteome seems to be rather limited, but our results also pinpoint several cases where AS could have a major impact on the function of a protein domain.nnAVAILABILITY AND IMPLEMENTATION: The JAVA implementation of AstaFunk is available as an open source project on http://astafunk.sammeth.net.nnSUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}